
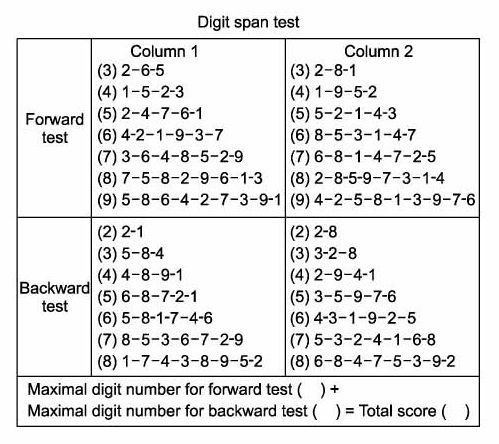
Directions Listen carefully as I say some numbers. Digits forwards Start Item A Finish Failure on both trials of a pair. The Digit Sequence test is an effective way to explore the labyrinths of. Indeed, classification statistics produced in this pediatric sample compare favorably with those produced in many real-world adult patients. THE DIGIT MEMORY TEST An assessment procedure for specialist teachers to investigate verbal memory difficulties in children’s learning. Results show that the digit span increases with age and correlates with intelligence. This means that when the longest repeated sequence is 7, the participant reached level 7 in one of trials. In the data-file the sequences are referred to as levels. The DST-score is an indication of intelligence among other tests. Although only moderately sensitive, Digit Span scores are likely to have good utility in identifying noncredible performance in relatively high-functioning older children and adolescents. The Digit Span score is the length of the longest correctly repeated sequence. For Reliable Digit Span, the optimal cut-score was ≤6, with sensitivity of 51% and specificity of 92%. For age-corrected scaled scores, a score of ≤5 resulted in the optimal cut-score, yielding sensitivity of 51% and specificity of 96%.
Fourteen percent of the participants failed both the Medical Symptom Validity Test and Test of Memory Malingering, which was used as the criterion for noncredible effort. The sample consisted of 274 clinically referred mild traumatic brain injury patients aged 8 through 16 years. The present study examined the classification value of several scores derived from the WISC-IV Digit Span subtest.
Although several recent studies have demonstrated the appropriateness of using stand-alone symptom validity tests with younger populations, a near absence of pediatric work has investigated embedded validity indicators.
#DIGIT SPAN TEST SCORE INTERPRETATION CODE#
Read more Source code JavaScript source code (digit-span-test. The scores were analysed as a function of gender and age. Participants see or hear a sequence of numerical digits and are tasked to recall the sequence correctly, with increasingly longer sequences being tested in each trial. of the two groups was compared on tests of working memory (Forward and Backward Digit Span. Use this information to interpret fluctuations in Index or Factor profile Step 6: Evaluate Subtest-Level Discrepancy Comparisons In some situations, the examiner may wish to compare two subtest scores. Far less work has focused on methods appropriate for children. A digit-span task is used to measure working memorys number storage capacity. In adult populations, research on methodologies to identify negative response bias has grown exponentially in the last two decades. Total number managed (ticks) backwards and forwards added together.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
